An FTP server is a type of server software that facilitates the transfer of files between a client and a server over a network using the File Transfer Protocol (FTP). It acts as a centralized storage location where users can upload, download, and manage files. In the guide, we will look at how to deploy an FTP server on Debian 12.
How to Install FTP Server
The easiest way to deploy an FTP server on Debian is to install and set up vsftpd package, which is a popular and secure FTP server.
Update the package list before you start installing new software:
sudo apt updateThen install vsftpd:
sudo apt install vsftpdAfter the installation is complete start the service:
sudo systemctl start vsftpdAnd enable vsftpd to start on boot:
sudo systemctl enable vsftpdTo check the current status of the vsftpd service launch the command:
systemctl status vsftpd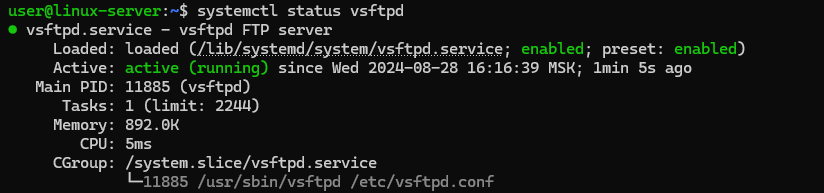
Creating an FTP Account and a Shared Directory
Now, after installing vsftpd, you need to create and configure an account and a directory that the FTP server will use.
The following command will add a new user account named ftp-user for example:
sudo useradd ftp-userThen create a home directory for ftp-user using mkhomedir_helper utility:
sudo mkhomedir_helper ftp-userAnd set the password for ftp-user:
sudo passwd ftp-userFor this tutorial we create a new directory:
sudo mkdir /ftp-directoryAnd set it as the FTP user home directory instead of the previously created one.
sudo usermod -d /ftp-directory ftp-userThe next command will change the ownership of the directory /ftp-directory so that it is owned by the user nobody and the group nogroup:
sudo chown nobody:nogroup /ftp-directoryAfter executing the following command, the ftp-user will become the owner of the /ftp-directory and the ftp-user group will be associated with it, granting the ftp-user and any other members of the ftp-user group the appropriate permissions to manage the directory and its contents.
sudo chown ftp-user:ftp-user /ftp-directoryConfiguring the FTP Server
To configure the FTP server navigate to /etc directory:
cd /etcOpen the configuration file using text editor nano:
sudo nano vsftpd.confModify the following lines in the configuration file:
listen=YES
listen_ipv6=NO
anonymous_enable=NO
local_enable=YES
write_enable=YES
dirmessage_enable=YES
use_localtime=YES
xferlog_enable=YES
connect_from_port_20=YES
xferlog_std_format=YES
chroot_local_user=YES
secure_chroot_dir=/var/run/vsftpd/empty
pam_service_name=vsftpd
allow_writeable_chroot=YESAlso set the range of ports, for example 37900–38000, the FTP server will use for establishing passive FTP data connections, which is essential for configuring both server security and network access control. To do this add the following strings to the end of vsftpd.conf file:
pasv_min_port=37900
pasv_max_port=38000When editing is complete, close the file and save the changes you have made.To apply the changes restart the vsftpd service:
sudo systemctl restart vsftpdConfiguring the Firewall
An FTP server uses multiple ports to facilitate communication between the client and the server:
- Port 20 is used for data transfer in Active FTP mode.
- Port 21 is used for the control connection in both Active and Passive FTP.
- A configurable range of ports used for data transfer in Passive FTP mode.
If you use Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) on your system, you need to add rules that allow access to the FTP server through these ports.
First, add rules that open ports 20 and 21:
sudo ufw allow 20/tcp
sudo ufw allow 21/tcpSecondly, create a rule for the port range that you specified in vsftpd.conf earlier:
sudo ufw allow 37900:38000/tcpChecking the Connection
To check the connection to the created FTP server, you can use various methods depending on whether you prefer command-line tools or graphical applications.
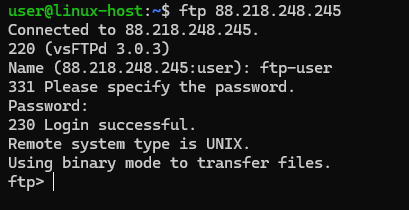
For example, in Linux system you can check the connection using the command in the terminal:
ftp X.X.X.XIn this case, change X.X.X.X to your FTP server IP address.
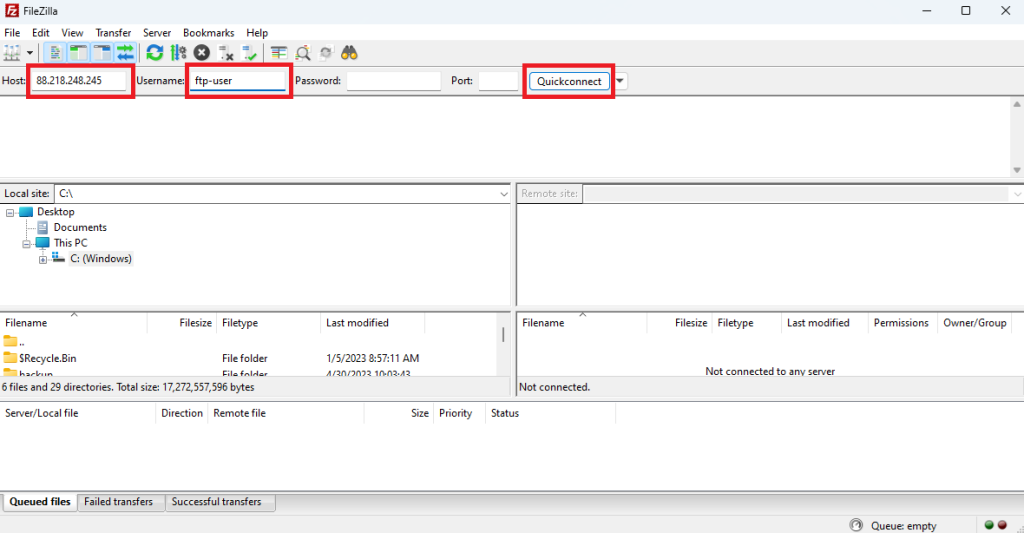
If you work on Windows and prefer to use GUI Tools, you can check the connection using a client such as FileZilla.
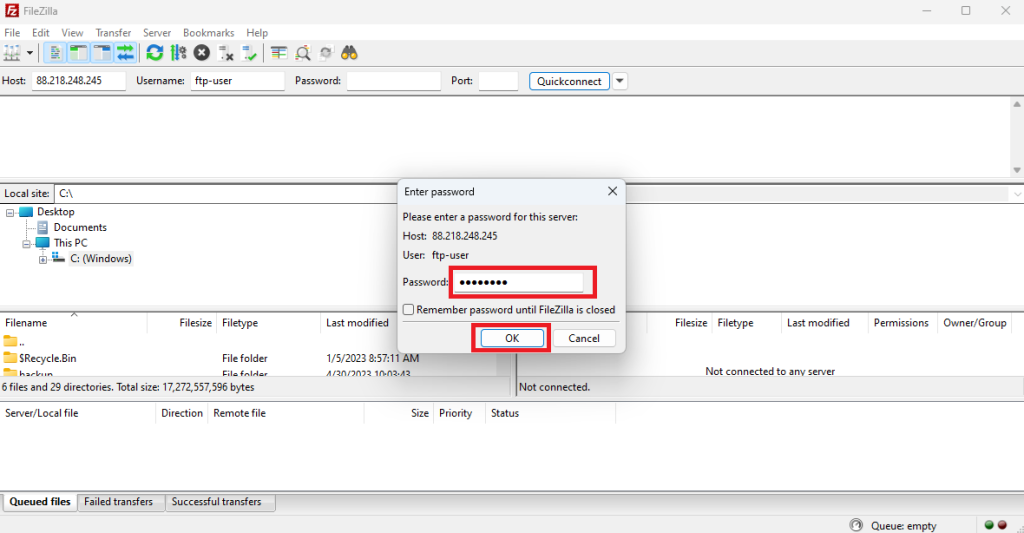
Open FileZilla, enter the FTP server IP address and username. Then click Quickconnect:
Then enter the FTP user’s password:
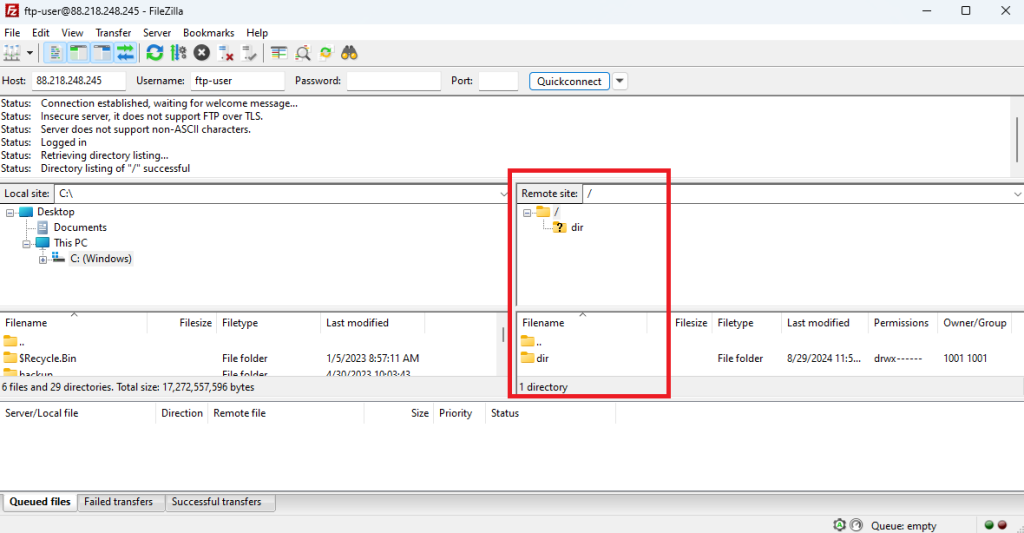
Once connected, the directories on the left side of FileZilla represent your local files, and the directories on the right represent the remote files on the FTP server.
Conclusion
After completing the steps described in this guide, you should deploy an FTP server on Debian 12 using vsftpd.
![]()